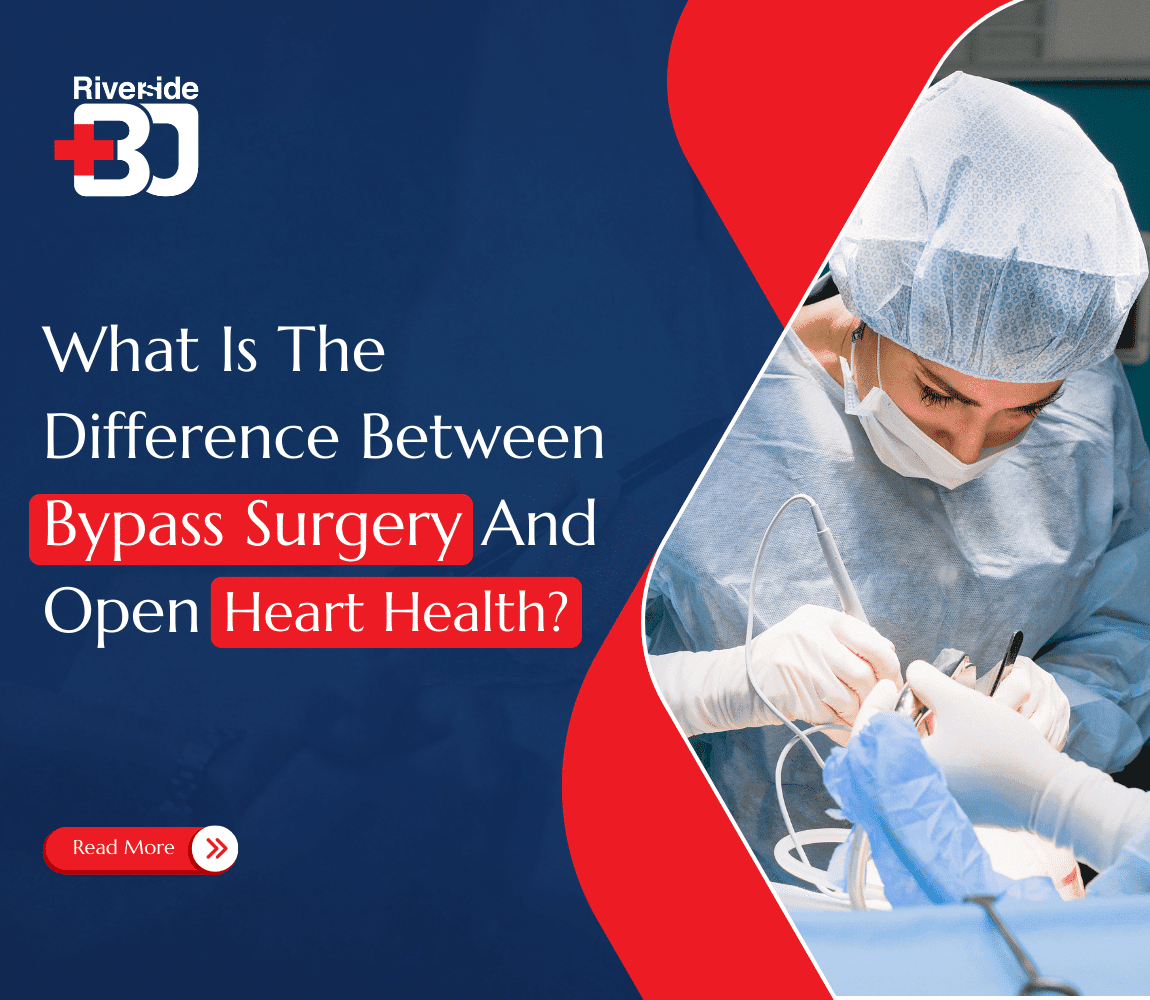
Ever wondered what the difference between open heart surgery vs bypass really is? While both are critical procedures for heart health, understanding their nuances can make all the difference in treatment.
In fact,
- Nearly 400,000 bypass surgeries are performed annually worldwide, with a significant portion requiring open-heart surgery.
This data highlights the widespread nature of these procedures, which are often the last line of defence for patients with severe heart conditions.
Open heart surgery vs bypass surgery share similarities, but each plays a unique role in treating heart disease.
So, in this article, we’ll dive into what each surgery entails, the difference between open heart surgery vs bypass, and when one might be recommended over the other.gery entails, the difference between open heart surgery vs bypass, and when one might be recommended over the other.
What is Open-Heart Surgery?
Before jumping into the difference between open heart surgery and bypass surgery, it is better to understand both individually.
Surgeons perform open-heart surgery by opening the chest and exposing the heart. They primarily use it to treat cardiovascular diseases, such as blocked arteries or heart valve issues.
The goal is to restore heart function, improve blood flow, and prevent future heart problems.
Now, let us take a detailed look at how surgeons perform it.
How Open-Heart Surgery is Performed
Doctors use open-heart surgery as a major medical procedure to treat various heart conditions, such as blocked arteries or faulty valves. It involves opening the chest to access the heart directly.
Hence, it allows surgeons to perform life-saving repairs with precision.
While both are critical cardiac procedures, understanding open heart surgery vs bypass helps patients better grasp their treatment options.
Let’s look at the detailed steps:
- Step 1: To begin with, the patient is placed under general anaesthesia to confirm that they are unconscious during the procedure.
- Step 2: Secondly, the surgeon makes an incision along the breastbone and opens the chest to access the heart.
- Step 3: The surgeon may temporarily stop the heart, and a heart-lung machine takes over its functions during the procedure.
- Step 4: The surgeon repairs or replaces damaged heart valves, bypasses blocked arteries, or performs other necessary surgeries.
- Step 5: Once the surgeons complete the surgery, they restart the heart and close the chest with sutures.
These steps outline the typical process involved in performing open-heart surgery. This further highlights the precision and care required at each stage of open heart surgery vs bypass procedures.
Understanding the difference between open-heart surgery vs bypass is essential. While bypass surgery focuses solely on rerouting blocked arteries, open-heart surgery covers a broader range of heart-related procedures.
This distinction helps patients better understand their treatment and recovery journey.
Recovery After Open-Heart Surgery
Recovery after open-heart surgery is a gradual process. Initially, patients may spend several days in the hospital’s intensive care unit (ICU). This depends on the complexity of the procedure in open heart surgery vs bypass cases.
Pain management and monitoring are critical during this phase. After discharge, doctors recommend physical therapy to help patients regain strength and mobility.
Additionally, most patients can return to normal activities after 6 weeks to 8 weeks, though full recovery may take several months. This depends on the type of procedure, especially when comparing open heart surgery vs bypass recovery timelines.
What is Bypass Surgery?
In the context of open heart surgery vs bypass, bypass surgery stands out as a preferred procedure. It reroutes blood around blocked or narrowed arteries to improve blood flow to the heart.
Doctors commonly perform it for people with coronary artery disease (CAD). In the debate of open heart surgery vs bypass, the goal of bypass surgery is to avoid obstruction. Subsequently, reducing symptoms and lowering the risk of heart attacks.
Types of Bypass Surgeries
To better understand the difference between open heart surgery vs bypass, let’s explore its types.
Different types of bypass surgeries target specific blockages and restore proper blood flow to the heart. Doctors carefully choose each procedure based on the patient’s condition, overall health, and surgical goals.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): This is the most common type. In this procedure, surgeons take a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body (usually the leg or chest) and use it to bypass the blocked artery.
- Off-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass (OPCAB): Secondly, the surgeon performs the surgery while the heart is still beating in this approach. Thus, this method reduces the risks associated with using a heart-lung machine.
- Minimally Invasive Bypass Surgery: This type uses smaller incisions and sometimes robotic assistance, aiming for quicker recovery and less scarring.
- Total Arterial Revascularisation: Arteries are used to create bypasses instead of veins in this procedure. As a result, this is more durable but also more complex.
Ultimately, understanding the variations in open heart surgery vs bypass helps patients make informed decisions. Therefore, choosing the right surgical approach fosters better outcomes and supports long-term heart health.
How Bypass Surgery is Performed
Bypass surgery is a life-saving procedure that improves blood flow to the heart. Knowing how bypass is done is important to understand the difference between bypass and open heart surgery.
- Step 1: Firstly, the medical team places the patient under general anaesthesia. The surgeon may opt for either a traditional or minimally invasive approach based on the patient’s needs.
- Step 2: Secondly, the surgeon makes a small incision in the chest or near the heart. The surgeon then identifies the blocked arteries.
- Step 3: The surgeon takes a blood vessel from another part of the body, like the leg or chest. Then, he grafts this vessel onto the coronary artery to bypass the blockage.
- Step 4: Once the bypass grafts are in place, the surgeon confirms that blood is flowing properly through the new pathways.
- Step 5: Lastly, the surgeon closes the incisions and takes the patient to recovery.
Understanding how bypass surgery works also helps clarify the open heart surgery vs bypass comparison. While bypass is one type of open-heart surgery, other heart conditions may require different procedures altogether.
Recovery After Bypass Surgery
When we compare the difference between open heart surgery and bypass surgery, the recovery time after bypass surgery varies from patient to patient.
Patients typically stay in the hospital for 4 to 7 days for monitoring. Furthermore, pain and fatigue are common, but medications help manage these symptoms.
Moreover, it usually takes 6 to 8 weeks before patients can resume most daily activities. A comprehensive rehabilitation program, including exercise and lifestyle changes, is essential for long-term recovery.doctor to align with your expectations. A second opinion can also be helpful for peace of mind and better decision-making.
Open Heart Surgery vs Bypass Surgery: Key Differences
Understanding the difference between bypass and open heart surgery can help patients make informed decisions about their heart health. While both involve critical surgical procedures, they serve different purposes and are used in distinct scenarios.
The main differences between open heart surgery vs bypass are:
- Purpose and Conditions Treated:
Open heart surgery is primarily used to treat conditions like:
- Congenital heart defects,
- Valve disorders, and
- Severe heart disease.
Furthermore, it may be necessary when other treatment options are insufficient. In contrast, bypass surgery specifically addresses coronary artery disease by redirecting blood flow to blocked arteries.
Both open heart surgery vs bypass surgery treat life-threatening conditions, but doctors choose them based on different patient needs.
- Procedure Differences:
The difference between open heart and bypass surgery can be better understood with their procedures. The procedure for open-heart surgery typically involves opening the chest and temporarily stopping the heart to repair or replace damaged structures.
In contrast, bypass surgery is less invasive. Surgeons use a blood vessel from another part of the body to bypass blocked coronary arteries.
Additionally, open-heart surgery often requires more extensive intervention, while bypass surgery can sometimes be minimally invasive.
- Recovery Time:
Recovery time for open heart surgery can be lengthy, usually requiring several weeks to months for full recovery. During this time, patients may need significant rest and rehabilitation.
While comparing the difference between open heart and bypass surgery, bypass surgery typically has a shorter recovery period. Many patients return to regular activities within 6-8 weeks.
However, both surgeries require follow-up care to ensure healing, prevent complications, and improve long-term heart health.
- Risk Factors and Complications:
In the comparison of open heart surgery vs bypass, open-heart surgery carries higher risks due to its complexity. It includes infection, bleeding, and complications from anaesthesia. Long-term risks can also include heart attack, stroke, and organ failure.
Furthermore, bypass surgery has fewer complications but may still present risks such as graft failure, infection, and blood clots.
The only common difference between bypass and open heart surgery is that both procedures require careful management. Hence, patients should follow their doctors’ advice to minimise risks.
When is Each Surgery Recommended?
Both open heart surgery vs bypass surgery are tailored to the patient’s condition. Deciding which surgery is necessary depends on various factors, including the type and severity of the heart problem.
- Open-Heart Surgery Indications:
Surgeons generally perform open-heart surgery to correct structural heart problems that medication or minimally invasive methods cannot treat. Therefore, it is essential for severe and complex conditions.
- Heart Valve Issues: In open heart surgery vs bypass, open-heart surgery may be required to repair or replace damaged heart valves. This procedure is often needed when valves no longer function properly.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Patients born with heart defects may need open-heart surgery to correct structural issues. Thus, ensuring proper heart function.
- Severe Aortic Disease: Doctors recommend open-heart surgery to prevent life-threatening complications like aneurysms when the aorta is severely damaged or diseased.
Ultimately, understanding the indications helps clarify the choice between open heart surgery vs bypass. Subsequently, this allows doctors to tailor the treatment plan based on each patient’s condition, urgency, and long-term outcomes.
- Bypass Surgery Indications:
Doctors most often recommend bypass surgery for patients with blocked coronary arteries. This is especially when symptoms persist despite medications or when multiple blockages put the patient at high cardiovascular risk.
- Severe Coronary Artery Disease: This bypass surgery is often performed when the coronary arteries become blocked. Consequently, it restricts blood flow to the heart muscle and causes chest pain or a heart attack.
- Angina Unresponsive to Medication: In open heart surgery vs bypass, if angina (chest pain) is not controlled with medications, bypass surgery is an option. It restores proper blood flow to the heart.
- Multiple Blockages: When there are several blockages in the arteries, bypass surgery may be the most effective option to bypass those blockages and improve heart health.
In assessing open heart surgery vs bypass, medical experts consider symptom severity, blockage extent, and overall health. This personalised approach ensures optimal treatment and better recovery outcomes for each patient.
Open Heart Surgery Vs Bypass: Factors To Consider
When choosing between open heart surgery vs bypass, it’s crucial to evaluate the severity of the heart condition. Your doctor will assess your overall health, heart function, and the type of blockages present. Here’s what you need to consider:
- Personal Health and Medical History:
Your medical history plays a significant role in deciding between open heart surgery vs bypass. If you have a history of other health issues, it may influence the decision.
In addition, doctors consider your age, fitness level, and previous heart treatments. How well you heal from surgery could impact the choice between open heart surgery vs bypass.
- Risk Factors and Recovery Time:
Another important factor is the recovery time and associated risks. Both open heart surgery vs bypass have different risks and recovery times. Bypass surgery tends to have a quicker recovery time compared to open heart surgery.
However, doctors must weigh the complexity of each surgery against your specific health needs. Your doctor will discuss which surgery best aligns with your recovery goals and potential risks.
- Consulting with Your Healthcare Team:
Consulting your healthcare team is essential for making the right decision. The input of cardiologists, surgeons, and specialists certifies that you fully understand the procedure and its outcomes.
Your doctor will explore open heart surgery vs bypass in detail to align with your expectations. A second opinion can also be helpful for peace of mind and better decision-making.
Why Choose Riverside B&J Hospital for Heart Care
At Riverside B&J Hospital, we are committed to providing world-class cardiac care with a focus on:
- Personalised treatment
- Cutting-edge medical technology
Our experienced team of cardiologists, led by Dr. Pritish Bagul and Dr. Vinay Jaiswal, makes sure that each patient receives the best possible care tailored to their unique needs.
From diagnostic services like angiography and ECG to advanced treatments such as bypass surgery and heart failure management. We provide comprehensive solutions for optimal heart health.
Furthermore, with state-of-the-art facilities, a dedicated cardiac ICU, and 24/7 emergency care, Riverside B&J Hospital is your trusted partner in heart health.
Conclusion: Open Heart Surgery vs Bypass Surgery
Choosing between open heart surgery vs bypass is a critical decision. It depends on various factors, including the severity of the condition, patient health, and surgical expertise.
Both procedures have their advantages, but consulting with a skilled cardiac team gives the best outcome for your heart health.
At Riverside B&J Hospital, we provide comprehensive guidance and support to help you make the right choice. Whether you need open heart surgery, bypass, or any other heart procedure, our team provides personalised care tailored to your needs.
FAQs about open heart surgery vs bypass1.
1. Is bypass surgery always a part of open-heart surgery?
Bypass surgery is often part of open-heart surgery, but not always. In many cases, open heart surgery involves separate approaches for different heart conditions.
2. What is the main difference between bypass and open-heart surgery?
The primary difference is that open heart surgery vs bypass depends on the condition being treated.
3. What is the difference between bypass and open-heart surgery when it comes to recovery time?
Bypass surgery generally has a quicker recovery time than open heart surgery. However, the recovery time can vary based on the individual’s health and the complexity of the procedure. This is especially when comparing open heart surgery vs bypass.
4. Can all bypass surgeries be minimally invasive?
Not all bypass surgeries can be performed minimally invasive. While some bypass surgery options are minimally invasive. It depends on the patient’s condition and the surgeon’s recommendation in the context of open heart surgery vs bypass suitability.
5. What are the risks associated with open-heart surgery?
Open-heart surgery comes with risks such as infection, bleeding, stroke, and heart attack. It’s important to weigh the potential risks before opting for open heart surgery procedures.